What are the completion requirements for the credit-bearing components of EQIPP courses?
The following are the completion requirements for the credit-bearing components of EQIPP courses.
| Credit Bearing
Component | Purpose | Completion Requirement |
| QI Basics Eligible for 2 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ | Present basic principals and concepts of quality improvement and introduce a systematic framework to guide improvement efforts. Note: You may only claim credit once, but you may revisit the course as often as you like as a refresher. QI Basics is available from all EQIPP courses. | Complete the QI Basics course, including the course evaluation. |
| CME Enduring Materials Credit Credit eligibility varies by course | Demonstrate compliance with the guidelines for the clinical topic and measure achievement of stated course objectives via an assessment. | Complete the assessments in the Clinical Guide tab for 1 or all key clinical activities. For maximum credit, complete all assessments for all key clinical activities. |
| CME Performance Improvement Credit Eligible for 20 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ | Demonstrate compliance with evidence-based performance improvement activities for the clinical content topic. Such improvement activities address a facet (i.e., structure, process or outcome) of a physician’s practice with direct implications for patient care. | Note: The American Board of Pediatrics (ABP) requires completion of two follow up data cycles to meet Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Part 4: Performance in Practice requirements. In EQIPP, a data cycle consists of Baseline data entry, an improvement plan, and followup data entry. You will be eligible to claim Performance Improvement (PI) Credit and notify the ABP upon completion of the 2nd follow up data cycles.
Within the My Improvement Project tab, a checkmark shows completed tasks in the left hand navigation. When you have completed a PDSA cycle for 2 improvement projects, you will be eligible to claim CME credit and notify the ABP of course completion. Use the Claim Credit link in the upper right corner to claim credit for the credit-bearing course components described in this table and print the certificate when desired. |
How long does it take to complete an EQIPP course?
You may progress through the course at a pace that is comfortable for you, taking into consideration the demands of your practice. Some EQIPP courses can be completed in as little as 120 days; others may span over 6 months or longer, depending on the number of improvement projects you create, the number of ideas for change you test, and the number of successful changes you implement in your practice to reach your desired aims. Specific EQIPP course expiration dates are listed on the EQIPP Home page under the My EQIPP Courses section.
Can subspecialists or non-practicing clinicians in need of recertification complete EQIPP courses for credit?
The answer is: Yes. Upon beginning an EQIPP course, you will be prompted to answer questions about having your own chart data to enter. Non-practicing clinicians (or those who see fewer than 10 patients per month) can use sample EQIPP data to complete the module and satisfy MOC Part 4 requirements. Such sample data can help illustrate the PDSA cycles of improvement, but cannot accurately reflect the level of care you provide to patients in practice.
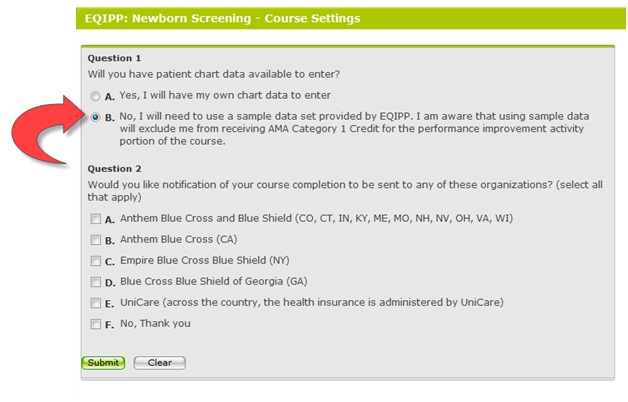
Of special note: Performance Improvement (PI) CME credit is only awarded to learners who collect, enter and analyze data. Using sample data provided by EQIPP excludes receipt of AMA Category 1 Credit for the performance improvement activity portion of the course. Use sample data to complete the course if you see fewer than 10 patients per month.
How do I learn more about individual EQIPP courses and/or register for them?
The PediaLink Online Learning Center is your online home for professional growth. Register for courses there or use the PediaLink CME Finder for more information about individual EQIPP courses before you register. (Alternatively, you may register for EQIPP courses at EQIPP.org.)
How can I learn about upcoming EQIPP modules and their release dates?
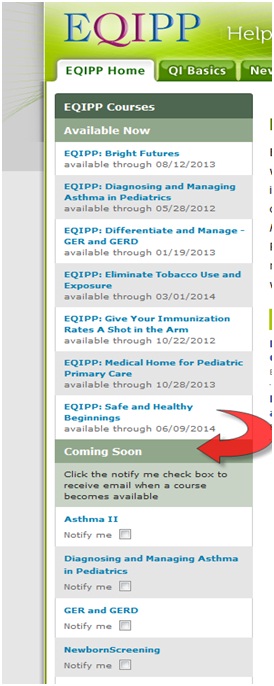
Check the Coming Soon section at www.eqipp.org for upcoming EQIPP course offerings and request to be notified via email of upcoming EQIPP courses that are of interest to you.
What are the technical requirements for EQIPP courses?
- Display: Resolution of 1024x786 pixels or higher
- Connection Speed: Broadband Internet access - 12 Mbps download/ 2 Mbps upload speeds.
- Internet Explorer 6.0, Firefox 2.0, Google Chrome, Netscape Navigator 7.0. It is recommended that AOL users do not use their AOL browser.
- Disable pop-up blocking software before entering EQIPP modules: Test your system for pop-up blocking. If no pop-up appears, follow your browser's directions for disabling your pop-up blocker.
- If you're still having problems viewing pop-ups after following the above directions, please contact Customer Service via e-mail at [email protected].
Software Add-Ons
- Adobe Acrobat Reader 5 required. Click here to download the plug-in.
- Flash 5 plug-in required. Click here to download the plug-in.
- Windows Media Player 10 or Real Player. Click here to download the free Windows Media Player 10. Click here to download the latest Real Player.
Direct additional related questions to the EQIPP Administrator at [email protected].
How much does EQIPP cost?
Enrollment fees are charged on a per course basis. The fees for each EQIPP course are as follows:
- Individual AAP Member Enrollment: $99
- Individual Non-Member Enrollment: $129
- AAP Resident Member Enrollment: $10
- AAP Fellow in Training Member Enrollment: $59
- AAP Member Group Enrollment (2 or more people): $79 / person
- Non-Member Group Enrollment (2 or more people): $119 / person
- AAP Resident Member Group Enrollment: $10 / person
- AAP Fellow in Training Member Group Enrollment: $59 / person
Large group and multi-course group enrollment discounts are available.
Group Enrollment Questions
Is there a special group rate for EQIPP courses?
EQIPP group enrollment fees are charged on a per course basis. The following fees apply for one EQIPP course:
- AAP Member Group Enrollment (2 or more people): $79 / person
- Non-Member Group Enrollment (2 or more people): $119 / person
Call 1-800-433-9016, EXT 7919 for group registrations. Large group and multi-course group enrollment discounts are available. Be sure to obtain the first and last name, AAP ID #, ABP ID #, and a contact email address from all group members before calling to register as a group.
Can my practice/hospital be invoiced for group enrollment?
Most EQIPP group enrollments are paid via credit card over the phone at the time of registration. If you have a large group or practice to enroll (10 or more people) and need a purchasing order or invoice for the registration fees in advance, call 1-800-433-9016, ext 7919. Also inquire about large group and multi-course group enrollment discounts.
What information is required to enroll a group?
To enroll a group, obtain each member’s first and last name, AAP ID #, ABP ID #, and contact email address before calling 1-800-433-9016, ext 7919 to provide this information. Large group and multi-course group enrollment discounts are available.
What if some members of my group do not have AAP IDs?
AAP membership is not required to obtain an AAP ID. Individuals can create their unique AAP ID at https://www.nfaap.org/netFORUM/eweb/. Click on My Account. Use the New Customer Registration link.
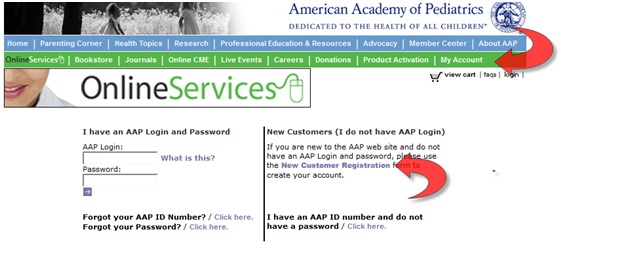
Once an individual has created an AAP ID, use this number to register for and log into the registered EQIPP or PediaLink course.
Can I add more people to my group at a later date?
Yes. Call 1-800-433-9016, ext 7919. Before calling, please obtain the first and last name, AAP ID #, ABP ID#, and email address from all new group member additions.
Help for Registered EQIPP Users
I've successfully registered for an EQIPP course online. How do I access it?
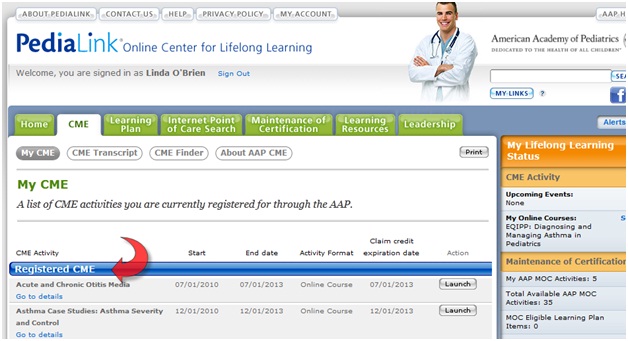
Following course registration, access the EQIPP course by logging in to PediaLink Online Learning Center. Go to the CME tab and look under the Registered CME Activities. Click the desired Launch button.
I accidentally registered myself as a non-clinician. How can I use/enter my own data?
Click the Settings link in the upper right corner and answer Yes to the question, “Will you have patient chart data available to enter?” Click Save.
How can I monitor my progression through the course?
Click Course Status in the upper right corner. A drop-down box displays a checkmark beside the My Improvement Project tasks and Assessments you have completed. If you have fulfilled CME credit requirements, the link to claim credit will be active. The last pages visited in the Clinical Guide are also indicated to help you continue working from where you left off.

I've finished entering follow-up data but am unable to analyze results or close the data cycle. How do I continue?
Go to My Improvement Project and click Collect Follow-up Data in the right navigation panel. The Patient Data Entry Status box shows the number of patients currently entered as well as the minimum number of patients that must be entered to close the data set. When are ready to close the sample data set (that is, you have entered the minimum number of patient, you intend to close the data set to future submissions, and you are ready to analyze and evaluate the results), click Close Data Set and Submit for Analysis.
I've completed my EQIPP course. How do I notify the ABP to update my MOC portfolio?
Use the Claim Credit link in the upper right corner to claim credit for completed credit-bearing course components and print related certificates when desired. Also see “What is required to complete an EQIPP course?”
I've completed the EQIPP course. How do I notify the ABP to update my MOC portfolio or print the completion certificate?
Click the Claim Credit link in the upper right corner and then click the Claim ABP MOC Credit link. This notifies the ABP to update your MOC portfolio.
Note: The Claim ABP MOC Credit link is not active until all course requirements are met. See the FAQ, “What are the completion requirements for the credit-bearing components of EQIPP courses?” for more information.
I've tried to electronically notify the ABP for my MOC and received an error message. What do I do now?
If clicking the Claim ABP MOC Credit link in EQIPP results in an error message, try notifying the ABP using the Manage ABP-MOC Credit tab on your PediaLink transcript page. If unsuccessful, use the Contact Us form located at the top of your EQIPP course. Include your full name, AAP ID number, ABP ID number, and a description of the error message (as described in the Reason column).
I've completed the EQIPP course. How do I claim CME credit?
Use the Claim Credit link in the upper right corner to claim credit for various credit-bearing components of EQIPP and to print related certificates.
How do I report a general technical issue with an EQIPP course or send my feedback to the AAP?
To report a general technical issue or send us feedback or feature requests, use the Contact Us link located at the top of any EQIPP course page.
What is the function of the Clinical Guide?
The Clinical Guide helps acquaint you with the key clinical activities – what they are, why they are important, and how to provide optimal care delivery. The Clinical Guide provides relevant background information and includes evidence-based guidelines, scientific recommendations, best practices, related tools and resources, and more.
What is the purpose of a baseline measurement?
To begin your quality improvement efforts in EQIPP, a baseline measurement identifies your current level of care in key clinical activities and identifies any gaps. This provides useful information for starting an improvement project. For example, after analyzing baseline data, you may choose to develop an improvement project that addresses:
- The biggest gap
- The easiest gap to bridge or close
- The gap that the team is best equipped to handle now
- The gap that the team is most motivated to bridge or close
- The gap that will yield the most success so that others will come on board with the team’s QI efforts
The possibilities, like the need for continuous practice improvement, are endless.
When and how do I do a follow-up measurement?
After creating an improvement project to address gap(s) in key clinical activities, you will work offline to conduct small tests of change through Plan, Do, Study, Act cycles. Then, go to My Improvement Project and click Collect Follow Up Data in the right navigation panel. Enter follow-up data to measure if the change(s) you tested actually resulted in an improvement.
Repeat the steps of collecting data, analyzing results to identify gaps, refining/creating an improvement project, working offline to complete PDSA cycles, and entering follow-up data until you have achieved your goals of delivering optimal newborn screening care.
What is an improvement project and how do I create one?
An improvement project recaps the 3 fundamental components of the team’s plan:
AIM: What is the team trying to accomplish?
MEASURES: What is being measured / how will the team know that a change is an improvement?
CHANGES: What change(s) can the team make that will result in an improvement?
After completing a baseline or follow-up measurement, EQIPP walks you through the following sequential steps for creating an improvement project:
- Analyze data and identify gaps.
- Select the quality gaps (measures) for improvement.
- Create an aim statement.
- Develop and then specify ideas for change.
- Optionally, view and print the improvement project and then put it to work in practice. When you return to EQIPP, you will be prompted to note any progress you made with your plan.
Does EQIPP provide ideas for change based on gaps in measures?
Yes. EQIPP includes an Ideas for Closing the Gap Worksheet for each key clinical activity. It is available in Resources and is automatically available for viewing on the Specify Changes screen. In this step, you enter ideas for change describing the specific steps you will take to achieve your Aim.
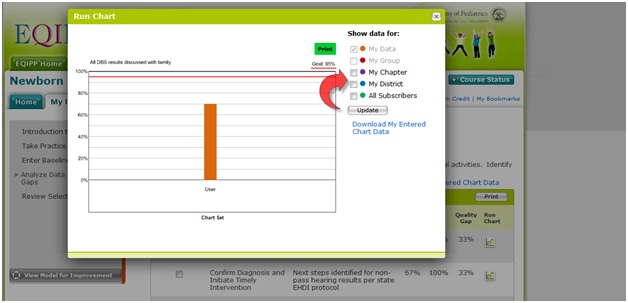
How do I analyze my data?
Analysis is based on quality gaps (measures) in key clinical activities. Identify the gaps (measures) your team wants to select for improvement. Use the checkboxes on the Analyze Baseline Data page to display your data along with corresponding data from the following course subscribers:
- All
- My state
- My district,
- My group, if you registered as part of a group,
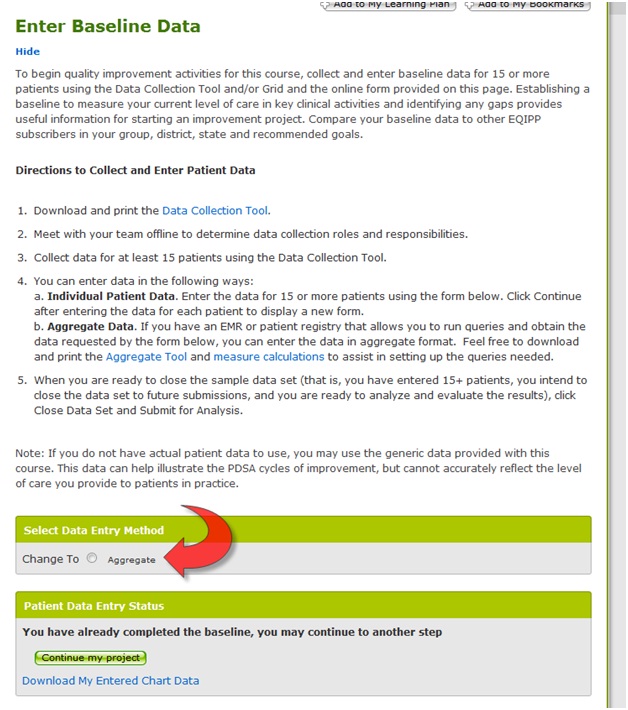
Will EQIPP allow me to enter aggregate data?
If you have an EMR or patient registry that allows you to run queries and obtain the data requested by the data collection tool, you can enter the data in aggregate format on either the Collect Baseline Data or Collect Follow-up Data page.
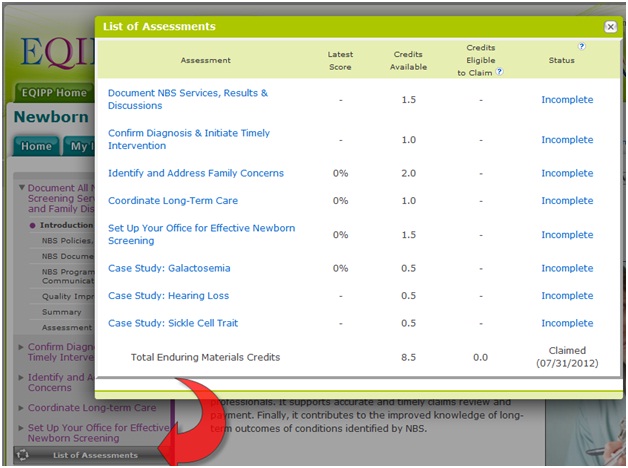
What are assessments in EQIPP? Will they help me earn CME Enduring Materials Credit?
Assessments are available on the Assessment tab in the Clinical Guide for all key clinical activities. They are designed to measure achievement of stated course objectives and to demonstrate understanding of the recommended guidelines for the clinical topic. Successful completion of assessments (a passing score of 70%) earns CME Enduring Materials Credit. You may complete an assessment for one or all key clinical activities. For maximum credit, complete all assessments for all key clinical activities.
EQIPP Frequently Asked Questions (QI Basics)
What is QI Basics?
The Quality Improvement in Pediatric Care, or QI Basics, course is a prerequisite for all Education in Quality Improvement for Pediatric Practice (EQIPP) courses and is included with the purchase of EQIPP courses. QI Basics presents fundamental quality improvement principles and concepts, designed to help pediatric providers address the gap in health care quality - the difference between current health outcomes and those thought to be achievable using best practice models and clinical practice guidelines.
QI Basics introduces the Model for Improvement, a “tried and true” systematic framework for improving patient care, as described in The Improvement Guide: A Practical Approach to Enhancing Organization Performance.
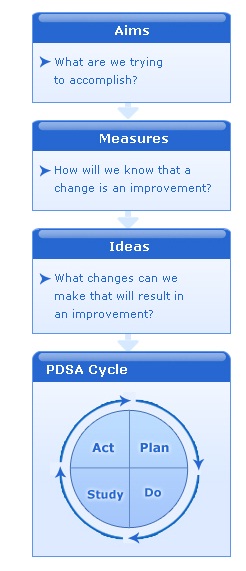
The Model for Improvement involves running small, successive tests of change through Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) cycles. PDSA cycles are used to quickly test ideas for change on a small scale to help you determine if the changes lead to improvement. Successful changes can be expanded to other areas or implemented throughout your practice.
What is the role of teams in QI?
Teamwork is a fundamental skill set underlying successful medical home improvement. Developing a team is the essential first step for you to take. Evidence shows that the positive results of practice improvement, including enhanced family-centered care, occur as a product of effective teamwork.
Teamwork involves a set of skilled, cross-disciplinary interactions that are learned, practiced, and continuously improved to provide better care delivery management, promote safety, and enhance outcomes. Highly functioning teams, made up of front-line caregivers, other staff members, and fully engaged family partners, have the capacity to quickly test ideas and continuously improve on them. Such a team has and cultivates an eye for future sustainability of efforts and has the know-how to systematically integrate widespread change into the practice culture.
Teams must gain leadership support and obtain practice-wide buy-in for innovations and procedural changes, thereby ensuring success. Effective teamwork requires collaborative approaches and mutual trust. This may involve a shift from a traditional hierarchical system of practice in which organizations have emphasized individual responsibility and accountability over the collective group.
What are PDSA cycles? What do the letters stand for?
Once your team has created an improvement project that includes an idea to try out, the next step is to test whether the idea for change leads to improvement. This is accomplished using 4 equally important steps: Plan, Do, Study, and Act. The PDSA cycle is used to conduct rapid tests of change on a small scale, learn from the results, and apply the learning to the next test cycle.
The cycle links the tests of change, refining the improvement project with each iteration until the redesigned project is ready for broad-scale implementation.
What is an Aim statement?
An aim statement answers the question, What are we trying to accomplish? It articulates the results you hope to see because of the changes you make. An aim statement should be carefully worded to include a description of how much improvement is desired, the specific population that is the focus of the improvement efforts, and the amount of time it should take to achieve the aim. An aim should be based on improvements you would like to see relevant to the quality gaps you identified.
The following are some characteristics of a good aim statement:
- Clear. You and your staff should be able to read the statement and understand, without interpretation, what you are trying to accomplish.
- Numeric. The aim statement includes quantifiable measures to track progress.
- A stretch. The aim statement includes a goal set high enough so achieving it will have a significant impact on patient care.
- Focused. By referring to the aim statement regularly, people involved in an improvement effort can avoid drifting away from the intent of the improvement project. Staying focused is important so that you and your staff do not become overwhelmed or discouraged by the work.
- Flexible. The aim statement should allow the improvement team to explore multiple solutions to the gap.