Blood pressure control in an 18-year-old with renal artery stenosis
The ABPM study was obtained to assess blood pressure control in a patient with severe unilateral fibromuscular dysplasia (FMD) treated on amlodipine at the time of the time of the study. Blood pressure control is variable with sympathetic nervous system stimulation (circle) resulting in marked blood pressure increase.
The ABPM parameters were set using the adult recommendations of 140/90 awake and 125/75 asleep.
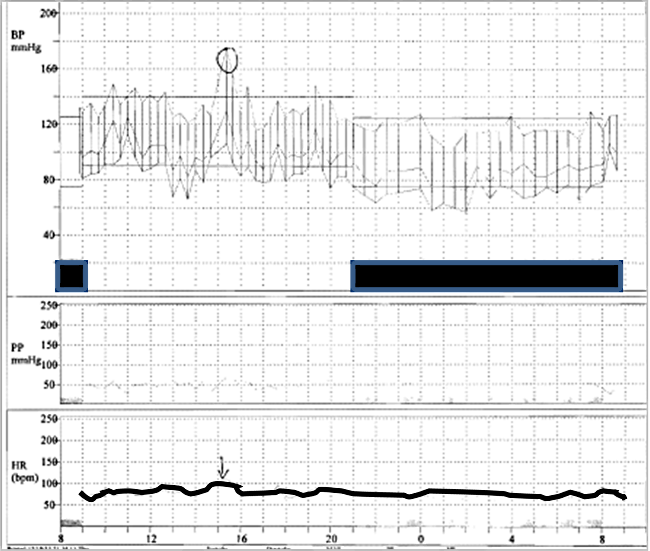
Summary sheet for 24-hour ABPM study:
| Statistical Summary |
Overall |
Awake |
Sleeping |
| Mean |
SD |
Range |
Mean |
SD |
Range |
Mean |
SD |
Range |
| Systolic |
127 |
13 |
104-175 |
134 |
12 |
116-175 |
118 |
7 |
104-132 |
| Diastolic |
81 |
12 |
57-113 |
87 |
10 |
66-113 |
73 |
10 |
57-102 |
| BP Load: Percent of readings above normal limits |
% Sleep Decline |
|
Awake |
Sleeping |
| Systolic |
22.9 |
24 |
12 |
| Diastolic |
34.3 |
32 |
16.1 |
Reference
Values |
Normal <25%
Intermediate 25%-50%
Abnormal >50% |
Normal ≥ 10% |
SD = Standard Deviation
Impression/Plan:
There are intermediate loads for awake and asleep diastolic blood pressures. The nocturnal dip is normal. Since this is unilateral renovascular mediated hypertension treatment with and ACEi or ARB rather than a calcium channel blocker is indicated. Further evaluation and therapy for the renal artery stenosis may be required.